Pure Red Cell Aplasia (PRCA) Treatment in India
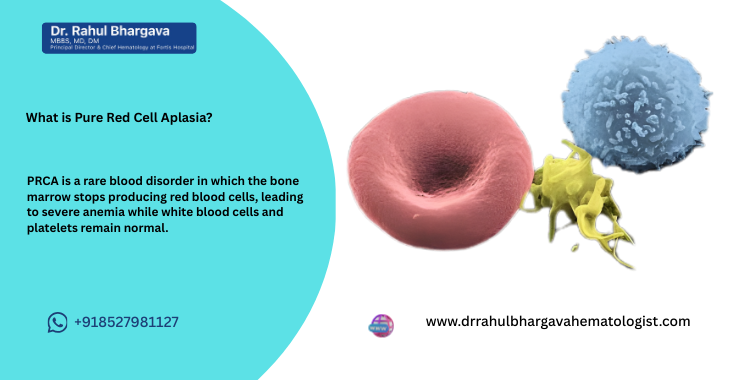
Pure Red Cell Aplasia (PRCA) is a rare blood disorder characterized by the selective failure of the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, leading to severe anemia. The term "pure" refers to the fact that only red blood cell precursors are affected, while other blood cell types, such as white blood cells and platelets, are typically produced normally. PRCA can be acquired or congenital and is often associated with immune system dysfunction, infections, or other underlying diseases.
What is Pure Red Cell Aplasia?
Pure Red Cell Aplasia (PRCA) is characterized by the failure of the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, resulting in severe anemia. Unlike other types of anemia, where a shortage of red blood cells occurs due to loss or destruction, PRCA is caused by a failure in the production of these cells. The condition can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired (developing later in life).
Types of Pure Red Cell Aplasia
PRCA can be classified into two main types:
1. Congenital PRCA
Congenital PRCA is an inherited condition where individuals are born with the inability to produce red blood cells. This type is extremely rare and often manifests in infancy or early childhood.
2. Acquired PRCA
Acquired PRCA occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow, leading to a halt in production. This form is more common and can be associated with various conditions, including autoimmune diseases, infections, or drug side effects.
Causes of Pure Red Cell Aplasia
The causes of PRCA can vary depending on whether the condition is congenital or acquired. Common causes include:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis can trigger PRCA.
- Infections: Parvovirus B19, HIV, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infections are often linked to PRCA.
- Drug Reactions: Certain medications, especially chemotherapy drugs, can damage the bone marrow and cause PRCA.
- Thymoma: A tumor of the thymus gland may cause immune-related PRCA.
- Other Hematological Disorders: Conditions like myelodysplastic syndromes can also contribute to the development of PRCA.
Symptoms of Pure Red Cell Aplasia
The main symptoms of PRCA are related to anemia and include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain (in severe cases)
These symptoms arise due to the body’s lack of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
How is Pure Red Cell Aplasia Diagnosed?
Early and accurate diagnosis of PRCA is essential for effective treatment. Dr. Rahul Bhargava follows a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, which typically includes:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can help identify anemia and the absence of red blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: A sample of bone marrow is taken to check for abnormalities in red blood cell production.
- Serological Tests: Tests to detect infections like Parvovirus B19 or other viral infections that may be causing the condition.
- Autoimmune Testing: To rule out underlying autoimmune diseases that may be triggering PRCA.
Treatment for Pure Red Cell Aplasia
The treatment for PRCA depends on the underlying cause and the type of PRCA. Common treatment options include:
1. Immunosuppressive Therapy
For acquired PRCA caused by autoimmune disorders, immunosuppressive drugs such as corticosteroids, azathioprine, or cyclosporine are often used to suppress the immune system and prevent it from attacking red blood cell precursors.
2. RBC Transfusions
In severe cases, red blood cell transfusions may be required to increase the number of red blood cells temporarily until the condition improves.
3. Thymectomy
For patients with PRCA related to thymoma, surgical removal of the thymus (thymectomy) may be recommended.
Why Choose Dr. Rahul Bhargava for Pure Red Cell Aplasia Treatment?
Dr. Rahul Bhargava is a leading hematologist in India, specializing in complex blood disorders like Pure Red Cell Aplasia. Here’s why patients choose him:
- Expertise in Hematology: Dr. Bhargava is known for his deep knowledge and experience in diagnosing and treating rare hematological disorders.
- Personalized Care: He tailors treatment plans according to the patient’s specific condition, ensuring optimal care and recovery.
- State-of-the-art Facilities: Dr. Bhargava practices at top-tier medical institutions equipped with advanced diagnostic and treatment technologies.
- Holistic Approach: Beyond medical treatment, Dr. Bhargava emphasizes patient education and holistic care to improve the quality of life during treatment.
- Multidisciplinary Team: He works with a team of specialists, including pathologists, immunologists, and transplant surgeons, to provide comprehensive care for PRCA patients.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
India offers high-quality medical care at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. The cost of PRCA treatment varies based on the specific interventions required. On average:
- Treatment Costs: Approximately ₹500,000 to ₹1,000,000 ($6,000 to $12,000).
- Accommodation: Ranges from ₹2,000 to ₹10,000 ($25 to $125) per day, depending on the facility.
These estimates can vary based on individual patient needs and the chosen healthcare facility.
Frequently Asked Questions
PRCA is a rare disorder where the bone marrow fails to produce red blood cells, leading to anemia.
Unlike other anemias that may affect multiple blood cell lines, PRCA specifically impacts only red blood cell production.
Acquired PRCA can result from autoimmune disorders, certain infections, medications, and thymomas.
Diagnosis involves blood tests, bone marrow examination, and serological tests to identify underlying causes.