Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) Treatment in India
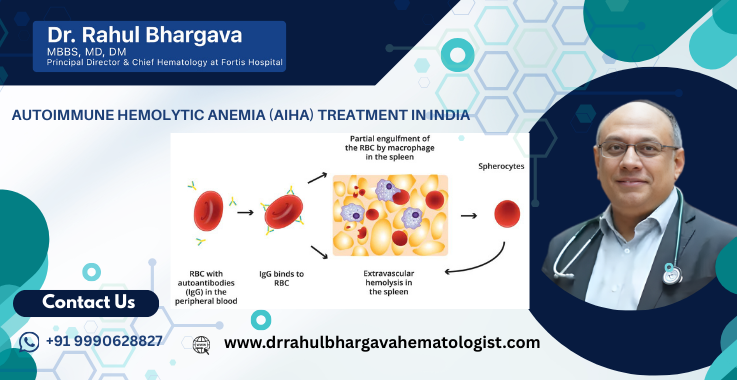
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition where the immune system attacks its own red blood cells, causing them to break down prematurely. It results in fatigue, jaundice, and shortness of breath, and can be acute or chronic. AIHA is categorized into Warm AIHA and Cold AIHA based on the temperature at which antibodies are most active.
India offers modern, effective, and affordable treatment for AIHA, with diagnostic evaluation costing $300–600, steroid therapy for as low as $50/month, and Rituximab therapy ranging from $2,000 to $3,500. Splenectomy, if needed, is also significantly more affordable in India ($3,000–5,000) compared to the West.
What is Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia?
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) is a rare blood disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly produces antibodies that attack and destroy its own red blood cells (RBCs). This destruction leads to hemolysis (breakdown of RBCs), resulting in anemia, fatigue, jaundice, shortness of breath, and pallor.
How many Types of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA)
AIHA is classified based on the type of autoantibody involved and the temperature at which these antibodies are most active:
| Type | Antibody Involved | Trigger Temperature | Common Causes | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warm AIHA (WAIHA) | IgG | 37°C (body temperature) | Idiopathic, lupus, lymphomas, drugs | Most common type (70–80% of cases); responds to steroids |
| Cold AIHA | IgM | Below 37°C | Mycoplasma pneumonia, EBV, lymphoproliferative disorders | Requires cold avoidance; responds to Rituximab |
| Mixed AIHA | Both IgG and IgM | Both | Rare | Harder to treat; needs combination therapy |
| Drug-Induced AIHA | Drug-dependent Abs | Variable | Penicillin, cephalosporins, quinine, methyldopa | Resolves upon stopping the offending drug |
Diagnosis and Evaluation
- CBC & Reticulocyte Count: Elevated reticulocytes, low Hb
- Peripheral Smear: Spherocytes, polychromasia
- Direct Coombs Test (DAT): Confirms autoimmune hemolysis
- LDH, Bilirubin, Haptoglobin: Elevated LDH, indirect bilirubin; low haptoglobin
- Cold agglutinin titer (if cold AIHA suspected)
- Screen for underlying causes: ANA, HIV, hepatitis panel, CT scan for lymphomas
What is the Treatment for Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA)?
Warm AIHA (WAIHA) – Most Common
First-line:
- Prednisone 1 mg/kg/day (taper over weeks to months)
- Folic acid and transfusions (as needed)
If steroid-refractory:
- Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody)
- Azathioprine, Mycophenolate, or Cyclosporine
- Splenectomy (rarely needed in the modern era)
Cold AIHA (Cold Agglutinin Disease)
Supportive care:
- Avoid cold exposure
- Blood transfusions (warm blood only)
Medications:
- Rituximab (first-line)
- Bendamustine + Rituximab (in lymphoma-related cases)
- Complement inhibitors (e.g., Sutimlimab – not widely available yet)
Drug-Induced AIHA
- Discontinue the offending drug
- Supportive care and steroids if severe
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA)
The symptoms of AIHA result from the rapid destruction of red blood cells and the body’s attempt to compensate. They can range from mild to life-threatening depending on the severity of hemolysis and how quickly it occurs.
Common Symptoms
- Fatigue or Weakness – due to anemia and reduced oxygen delivery
- Pale or Yellowish Skin (Jaundice) – caused by increased breakdown of hemoglobin
- Dark-colored Urine – due to excess hemoglobin released from destroyed RBCs
- Shortness of Breath – especially during physical activity
- Rapid Heartbeat (Tachycardia) – the heart compensates for reduced oxygen
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness – due to low hemoglobin and poor circulation
- Fever and Chills, especially during hemolytic crises
- Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly) – from overwork in clearing damaged cells
- Headache – linked to oxygen deficiency
- Cold Sensitivity – especially in cold AIHA (symptoms worsen with exposure)
Severe Cases May Show:
- Chest pain
- Confusion
- Signs of heart strain or failure (if untreated)
- Hemoglobinuria (blood in urine)
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) Treatment Cost Comparison: India vs Turkey vs USA
The total cost of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) treatment in India typically ranges from $2,000 to $6,000, depending on the severity, need for Rituximab, and whether splenectomy or long-term immunosuppressive therapy is required.
| Treatment Type | India (USD) | Turkey (USD) | USA (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Workup (CBC, Coombs, LDH, ANA, etc.) | $300 – $600 | $1,000 – $2,000 | $5,000 – $8,000 |
| Steroid Therapy (per month) | $50 – $100 | $200 – $300 | $1,000+ |
| Rituximab (4-dose infusion cycle) | $2,000 – $3,500 | $5,000 – $8,000 | $20,000 – $30,000 |
| Immunosuppressants (per month) | $100 – $300 | $500 – $700 | $2,000+ |
| Blood Transfusions (per unit) | $50 – $100 | $200 – $400 | $800 – $1,000 |
| Splenectomy (if needed) | $3,000 – $5,000 | $7,000 – $10,000 | $30,000 – $50,000 |
| Inpatient Hospital Stay (3–5 days) | $300 – $800 | $1,000 – $2,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Annual Monitoring & Follow-up | $500 – $1,200 | $1,500 – $2,500 | $10,000 – $20,000 |
Key Insight:
- India offers comprehensive and modern AIHA treatment at 70–90% lower cost than in the USA.
- Turkey serves as a mid-range option with an international medical infrastructure.
- USA prices are significantly higher, especially for immunotherapies and surgery.
Recovery Periods for AIHA
| Treatment Type | Expected Recovery Timeline |
|---|---|
| Steroid Therapy | Initial improvement in 1–3 weeks; full taper over 2–4 months |
| Rituximab Therapy | Hemoglobin stabilizes in 4–8 weeks after infusion cycle |
| Immunosuppressants | Gradual response in 1–2 months; maintenance may last 6–12 months |
| Splenectomy | Hospital stay: 3–5 days, full recovery in 2–4 weeks |
| Cold AIHA (with Rituximab + cold precautions) | Symptom improvement in 1–2 months; relapse monitoring ongoing |
Key Notes:
- Most patients begin to feel better within a few weeks of starting treatment.
- Warm AIHA often responds faster to steroids; cold AIHA requires longer monitoring.
- Lifelong follow-up may be required for chronic or relapsing cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
AIHA is a condition where the immune system attacks the body's own red blood cells, causing anemia. It can be categorized into warm or cold types based on the temperature at which the antibodies are active.
Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, pale or yellow skin, dark urine, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and sometimes an enlarged spleen or liver.
Diagnosis involves physical examination, complete blood count (CBC), Coombs test, peripheral blood smear, and sometimes bone marrow biopsy.
Treatments include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, IVIG, blood transfusions, plasmapheresis, and splenectomy. The approach depends on the severity and cause of the condition.
Treatment costs range from INR 1,00,000 to 6,00,000 (USD 1,200 – 7,200), depending on the case severity and required procedures like IVIG or surgery.