Beat Leukemia with CAR-T: A Revolutionary Leap in Blood Cancer Treatment
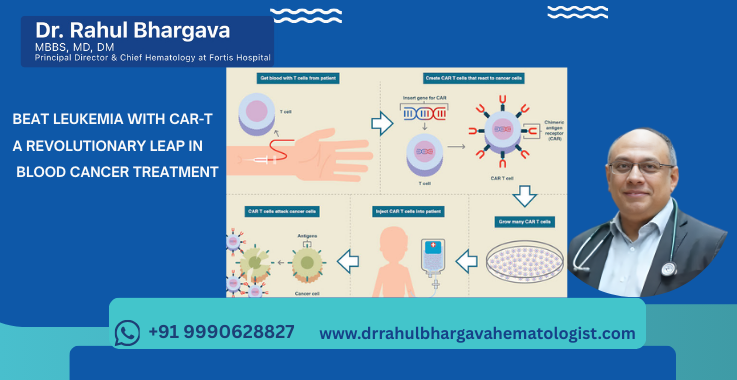
Table of Contents
Leukemia, a type of blood cancer, has long posed significant challenges to both patients and medical professionals. However, recent advancements in immunotherapy have opened doors to powerful new treatments. One such innovation is CAR-T cell therapy, a groundbreaking approach that has transformed the way certain types of leukemia are treated. This blog explores how CAR-T therapy is revolutionizing leukemia care, who it’s for, how it works, its success rates, cost, side effects, and why it’s considered a beacon of hope for patients around the world.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell) therapy is an advanced form of immunotherapy that modifies a patient’s own T cells to fight cancer more effectively.
How It Works:
- T cell collection – Blood is drawn from the patient and T cells (a type of white blood cell) are separated.
- Genetic modification – In a lab, these T cells are re-engineered to produce special receptors (CARs) on their surface.
- CARs target cancer – These new receptors allow the T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Cell infusion – The modified CAR-T cells are multiplied and infused back into the patient’s bloodstream, where they seek and destroy leukemia cells.
Types of Leukemia Treated with CAR-T
Currently, CAR-T therapy is approved and most effective for certain types of relapsed or refractory leukemias, including:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) – Particularly in children and young adults.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) – Especially in cases resistant to standard treatment.
- Other B-cell leukemias – Where CD19 is present on the leukemia cells (CAR-T therapies often target the CD19 protein).
Who is Eligible for CAR-T Therapy?
CAR-T is generally reserved for patients who:
- Have relapsed (the leukemia came back) or refractory disease (did not respond) to standard treatments.
- Are physically fit enough to undergo the therapy and handle possible side effects.
- Have CD19-positive leukemia (in case of CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy).
Pediatric patients with B-ALL have shown especially promising results with CAR-T therapy.
Benefits of CAR-T Therapy for Leukemia
- High remission rates – Up to 80-90% complete remission in some pediatric ALL patients.
- Personalized treatment – Uses the patient’s own immune cells.
- Minimally invasive – Involves infusions rather than extensive surgery.
Long-lasting immunity – T cells may continue to patrol the body, offering continued protection.
CAR-T vs. Traditional Leukemia Treatments
- Aspect CAR-T Therapy, Chemotherapy, Bone Marrow Transplant
- Precision, highly targeted Broad, Dependent on donor match
- Immune system involvement: Uses its immune cells.s Often suppresses the immune system. Can rebuild the immune system
- Side effects: Immune-related (manageable) Hair loss, infections, etc. Graft vs. host risk
- Suitability For relapsed/refractory cases, First-line treatment is often used after relapse
Potential Side Effects of CAR-T Therapy
While CAR-T is promising, it is not without risks. Common side effects include:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) – A strong immune response that can cause fever, low blood pressure, and breathing difficulties.
- Neurotoxicity – Temporary confusion, headaches, or seizures.
- Low blood counts – Due to immune cell activity.
- Infections – As immunity may be temporarily compromised.
Note: These side effects are closely monitored and often manageable with medications like tocilizumab or steroids.
CAR-T Therapy Success Stories
Many patients who had no remaining treatment options have experienced complete remission after CAR-T. For example:
- A 7-year-old child with relapsed ALL went into complete remission just weeks after CAR-T treatment.
- Adults with CLL who failed multiple therapies have achieved long-term disease control.
These stories illustrate the real-world effectiveness and hope that CAR-T brings.
CAR-T Therapy Cost in India and Globally
India:
- Cost ranges between INR 35–60 lakhs ($40,000–$70,000), significantly lower than in Western countries.
- India’s leading hospitals are now offering CAR-T under clinical trials and approved therapies, making it affordable for international patients.
USA/Europe:
- Costs can exceed $450,000 per treatment cycle.
- High insurance and infrastructure costs contribute to the price.
Top Hospitals in India Offering CAR-T Therapy
- Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai
- AIIMS, Delhi
- Apollo Hospitals
- Narayana Health
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram
These centers are at the forefront of CAR-T research, trials, and treatment delivery, making India a growing hub for medical tourism.
Is CAR-T a Cure for Leukemia?
While it’s not guaranteed to cure all cases, CAR-T therapy offers a significantly higher chance of long-term remission in patients who otherwise had few options. In some cases, it eliminates all traces of cancer.
Future of CAR-T in Leukemia Treatment
The scope of CAR-T therapy is expanding:
- Next-gen CARs – Targeting multiple antigens to avoid relapse.
- Off-the-shelf CAR-T – Using donor cells to make treatment more widely available.
- Combination therapies – With checkpoint inhibitors and targeted drugs.
Conclusion: A New Era in Leukemia Treatment
CAR-T therapy is more than just a treatment—it’s a game-changer in the fight against leukemia. With its ability to retrain the immune system to destroy cancer cells, CAR-T offers hope to those who’ve exhausted all other options. As research advances and costs decline, this therapy is poised to become a mainstay in leukemia treatment worldwide, especially in countries like India where cutting-edge care is becoming more accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions
CAR-T cell therapy for leukemia uses genetically modified T-cells to target and kill cancer cells, offering high remission rates in relapsed or refractory cases.
CAR-T therapy is most effective for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and certain relapsed blood cancers.
CAR-T therapy shows upto 90% remission rates in eligible leukemia patients who have failed conventional treatments.
CAR-T therapy is safe when performed at specialized centers, though patients are closely monitored for side effects like cytokine release syndrome.
